In Imaging Anatomy: Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis (Second Edition), 2017. In addition, you might want to watch our anatomy and physiology lectures on YouTube, or check our anatomy and physiology notes. (The apical pulse is located at the midclavicular line of the 5th intercostal space, as demonstrated by Nurse Sarah in our Apical Pulse Assessment video.). However, the facet for rib seven is usually shared by both the body and xiphoid process, with each part containing only a partial facet. The bilateral mesenchymal precursors of the sternum develop immediately ventral to the primordia for the clavicle and ribs but are in fact independent from them in their development (Gumpel-Pinot, 1984). The presternal mass (median sternal anlage) lies inferior to the paired suprasternal masses and will eventually fuse with all but the most lateral part of the suprasternal section to form the upper part of the manubrium, while the remainder of the two lateral masses take part in the formation of the sternoclavicular joint (Whitehead and Waddell, 1911; Jewett et al., 1962; Klima, 1968; Eijgelaar and Bijtel, 1970). In young individuals it is composed of six segments. Superior and inferior views of the right ribs. All rights reserved. Frank H.Netter MD: Atlas of Human Anatomy, 5th Edition, Elsevier Saunders. The sternum is divided into three regions: The manubrium is the most superior region of the sternum and articulates with the clavicles or collarbones and the first pair of ribs. Each rib articulates posteriorly with the vertebrae, and the first 10 ribs articulate anteriorly with the sternum. Ribs one and two articulate with the manubrium, but rib two articulates with only a partial facet of the manubrium at the sternal angle.
The word xiphoid comes from the Greek word for sword-shaped, which describes its thin and pointed shape. It is a flat bonethat articulates with the clavicle and the costal cartilages of the upper 7 ribs (true ribs), while the 8th, 9th and 10th ribs (false ribs) are indirectly attached with sternum via costal cartilage of the ribs above. The body or middle portion of the sternum serves as the anterior attachment for ribs 2 through 7. In an infant animal model of CPR, this two-thumb method of compression with thoracic squeeze resulted in higher systolic and diastolic blood pressures and a higher pulse pressure than traditional two-finger compression of the sternum.156 Although not rigorously studied, our clinical experience indicates that it is very difficult to attain adequate chest compression force and adequate aortic pressures with the two-finger technique, so we fully support the AHA Guidelines for health care providers to perform CPR on infants with the two-thumb-encircling hands technique.157, Gregory D. Cramer, in Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and Ans (Third Edition), 2014. The superior sternopericardial ligament connects the pericardium (that lies in the superior part of the middle mediastinum) to the manubrium. The sternum is highly vascular in nature and covered with a thin layer of compact bone providing a degree of flexibility. Thats what this part is: a little projection coming off the inferior portion of the sternum. Due to their direct connection and proximity, the ribs are also commonly fractured in the process. This is an uncommon fracture, and due to its location to the great vessels, is potentially rapidly dangerous.  The lateral margin is notched for articulation with costal cartilages of ribs. This technique can be used for coronary artery surgery, and open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.
The lateral margin is notched for articulation with costal cartilages of ribs. This technique can be used for coronary artery surgery, and open abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.
The sternum is classified as a flat bone, and it makes up part of the axial skeleton.
The inferior process of the sternum is the xiphoid process.
In some cases, there may be an extra pair of ribs or a pair of missing ribs, most often in the cervical or lumbar area. Symptoms will include soreness around the area, and if the great vessels are compromised, sudden death. The anatomy of a typical rib (any rib from 3 to 9) is given in Fig.1.7.36.
Located below the manubrium, the gladiolus is the longest portion of the sternum and articulates with the ribs, either directly or indirectly, through the costal cartilage.
The sternum was originally considered to be an embryological derivative of the mesenchymal somite arrangement that gives rise to the vertebral column, ribs, intercostal and anterior abdominal musculature.
This section focuses on the sternum and ribs, because the thoracic vertebrae have already been presented. The chest is shaped like a birds, this condition is also a feature in many syndromes like Downs syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Reviewer: It has facets on its each lateral border for articulation with the costal cartilage of the 3rd to 7th ribs along with the part of second costal cartilage. Most primates do not fuse the sternum as we tend to, so their thorax will be more flexible than ours. The diagnosis can be suspected on a PA radiograph from the steep inferior slope of the anterior ribs and undue clarity of the lower dorsal spine seen through the heart. They mostly reffer to the deviations of the shape of the sternum, which in some cases, especially if it is an extreme deviation, can affect the organs within thoracic cavity. Uruj Zehra MBBS, MPhil, PhD The ventral domain courses toward the neck between the costo-chondral junctions and the sternum. Paul Jackson Mansfield DPT, BS, MS, Donald A. Neumann PhD, PT, FAPTA, in Essentials of Kinesiology for the Physical Therapist Assistant (Third Edition), 2019, The sternum, often called the breast bone, is located at the midpoint of the anterior thorax and is composed of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process (Fig. 4.3). See our full, Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window), Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window), Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window), Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window), Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window), Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window), Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window), Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window), Click to share on Skype (Opens in new window), Not Smart Enough for Nursing School? There are certain congenital pathological conditions related to the sternum. The letters MBX, just like the Honda motorcycle brand, can help you remember the order of the parts of the sternum (from top to bottom). At approximately 6 weeks of fetal life a pair of lateral sternal plates can be identified embedded in the anterior chest wall, which are independent of both each other and the developing ribs (Fig. The thin, pointed xiphoid process forms the most inferior region of the sternum to which the costal cartilage and cartilage of the celiac, or solar, plexus attaches. The lung is vulnerable here and may be punctured from the anterior in this region.
Lateral to the jugular notch is the clavicular notch, which projects superolaterally, allowing its concavity to articulate with the clavicle. The body of the bone (also known as the gladiolus) is a long flat structure, with a convex anterior surface, and a concave posterior surface.
The sternum develops from left and right bars of mesenchyme that migrate to the midline and eventually fuse.
Copyright 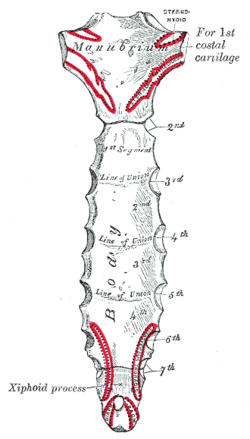 By accessing any content on this site or its related media channels, you agree never to hold us liable for damages, harm, loss, or misinformation. However, as minimally invasive radiologically guided techniques such as EVAR (endovascular aneurysm repair) have developed, sternotomy is being used less and less.
By accessing any content on this site or its related media channels, you agree never to hold us liable for damages, harm, loss, or misinformation. However, as minimally invasive radiologically guided techniques such as EVAR (endovascular aneurysm repair) have developed, sternotomy is being used less and less.
The first forms the manubrium, the second to fifth fuse and form the corpus, and the sixth forms the xiphoid process.
Author:
The opposite pattern is found in the first rib, The head lies medially and the tubercle inferiorly, except for the first rib, on which the head points inferiorly, The sternal end is flat with a U-shaped depression and lies anteriorly. Each rib articulates posteriorly with the vertebrae, and the first 10 ribs articulate anteriorly with the, Structure and Function of the Shoulder Complex, Essentials of Kinesiology for the Physical Therapist Assistant (Third Edition), -shaped bone that acts like a mechanical rod that links the scapula to the, Imaging Anatomy: Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis (Second Edition). Encircling ribs send out cartilaginous growths that join with the sternal bars.
The superior and inferior glenoid tubercles border the superior and inferior aspects of the glenoid fossa and serve as proximal attachments for the long head of the biceps and the long head of the triceps, respectively. The second costal cartilage articulates with the sternum at this angle. The ventral domain courses over and embeds the costal cartilages, and the muscles found between the costal cartilages the parasternal interchondral muscles.
Mitchell: Grays Anatomy for Students, 2nd Edition, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier.
At birth, it is a thin, roughly triangular region of cartilage that slowly ossifies into a bone and fuses with the body of the sternum. The vital organs can be compromised. The manubrium is the most superior portion of the sternum that articulates with the clavicleforming the sternoclavicular (SC) joint.
Chummy S.Sinnatamby: Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied, 12th Edition, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier. Three mesenchymal masses appear at the superior extremity of the lateral plates around 6 weeks of fetal life. Take a free sternum anatomy quiz to test your knowledge, or review our sternum anatomy video. The xiphoid process is made of cartilage until around middle age, at which point it finally becomes bone. The sternum develops from a left and right cartilaginous plates that unite in the midline. The sternum is a complex bone that I suspect is an interloper in the ventral domain. The manubrium attaches to the body of the sternum, or gladiolus, at a transverse ridge, forming the sternal angle (also known as the angle of Louis).
Lateral chest radiography is orthogonal (at 90) to PA chest radiography. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. The slightly concave anterior aspect of the bone is called the subscapular fossa, which allows the scapula to glide smoothly along the convex posterior rib cage. Here's the truth #shorts, Glasgow Coma Scale Assessment Nursing NCLEX Mnemonic, 3 Pulse Sites You MUST Know as a Nurse #shorts, Skin Glands Anatomy: Sweat Glands, Sebaceous Glands Integumentary System, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Assessment Nursing NCLEX Review, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) NCLEX Questions Quiz Nursing, The manubrium comes from a word that means handle, The gladiolus (body) comes from a word meaning sword, Xiphoid comes from an ancient word that means straight sword.  This may be an isolated abnormality or it may be associated with other disorders such as Marfan syndrome or congenital heart disease (particularly atrial septal defect [ASD]).
This may be an isolated abnormality or it may be associated with other disorders such as Marfan syndrome or congenital heart disease (particularly atrial septal defect [ASD]).
Pectus excavatum is a condition also known as funnel chest, where the sternum and superior ribs grow abnormally, created a sunken chest appearance.
Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org.
Figure 7.4. The ribs develop from their ossification centers and unite with the sternum in the midline. Kenhub. Around the ninth fetal week, the sternal plates begin to fuse with each other in the midline and do so in a craniocaudal direction (Ogden, 1979: England, 1990). The line of division between the somite-derived structures and the lateral plate mesodermal structures is the future chondrosternal junction (Ogden et al., 1979a). The thoracic cage gradually broadens from superior to inferior and flattens from anterior to posterior. The sternal fibers of pectoralis major and sternocleidomastoid are attached to the anterior surface. It forms part of the rib cage and the anterior-most part of the thorax. The inferior tip of the sternum is called the xiphoid process, meaning sword shaped.. Test what you've learned about the sternum with the following quiz: Open cardiothoracic surgery requires the sternum to be divided and splayed open to access the thoracic organs. The greater and lesser tubercles are divided by the intertubercular groove, often called the bicipital groove because it houses the tendon of the long head of the biceps. Moving onto the chest wall, the lateral border of this field is marked by the costo-chondral junction (i.e. The primary function of the sternum is the protection of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels from physical damage. This is the point where the 2nd pair of ribs attach to the sternum, with articulation at a partial facet, or demifacet, on the manubrium and another partial facet on the body of the sternum. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. Kim Bengochea, Regis University, Denver. Figure1.7.34.
The radiological signs on a posteroanterior (PA) chest radiograph consist of a shift of the heart to the left, straightening of the left heart border with prominence of the main pulmonary artery segment, loss of the descending aortic interface and an increased opacity in the right cardiophrenic angle, often accompanied by a loss of clarity of the right heart border which simulates right middle lobe disease. Michael A. Gropper MD, PhD, in Miller's Anesthesia, 2020, In adult and animal models of cardiac arrest, circumferential (vest) CPR has been demonstrated to dramatically improve CPR hemodynamics.155 In smaller infants, it is often possible to encircle the chest with both hands and depress the sternum with the thumbs, while compressing the thorax circumferentially (thoracic squeeze). How does this field traverse the thorax? Pectoralis major, a limb muscle, inserts on the sternal bars, so in the CF context the sternum is modelled as a ventral component of the pectoral girdle just as the scapula is a lateral/dorsal element. The newer approaches lead a shorter recovery time and less morbidity for the patient. The acromion process is a wide, flattened projection of bone from the most superior-lateral aspect of the scapula. The xiphoid process may take various shapes and allows the attachment of muscles of the abdomen.
The pre sternal mass appears later than the lateral sternal plates and it is thought to be embryologically derived from the pectoral girdle (Currarino and Silverman, 1958). All Rights Reserved. A rare condition of cleft sternum is strongly associated with ectopia cordis (Chang and Davis, 1961; Moore, 1988) and, not surprisingly, there is a strong correlation between developmental abnormalities in this region and congenital heart defects in general (Fischer et al., 1973; Lees and Caldicott, 1975). Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. Smooth inferior surface (no costal groove) and rough superior surface, Roughened tuberosity in place of the tubercle, No neck, tubercle, angle, or costal groove, The superior shaft surface is smooth and the inferior sharp. The sternum is used as the site for bone marrow biopsy in obese or overweight patients, where access to the iliac crest is limited. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Na Homolce Hospital, Prague, Czech Republic, Wroclaw Medical University, 50-367 Wrocaw, Poland, A Comprehensive Guide to Geriatric Rehabilitation (Third Edition), Various sternal deformities are described, and the most important radiologically is the depressed, In smaller infants, it is often possible to encircle the chest with both hands and depress the, Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and Ans (Third Edition), Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology Essentials, is the skeletal part of the thorax and consists of the, ). 7.4A: Thoracic Cage: Sternum is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. The sternal angle is located on a horizontal plane that posteriorly passes approximately through the level of the T4-5 IVD. 6-2).
First, if you look at the superior border, youll notice a notched area in the center, which is called the jugular notch or suprasternal notch. These muscles need explaining. Conversely, the internal intercostal is red fiber from the interchondral region ventrally to the rib angle, where it turns into an internal intercostal membrane as it courses toward the dorsal midline. 4.5) is the point of attachment for a multitude of ligaments and muscles.
This angle makes the sternum slightly convex anteriorly.
The medial and lateral borders of the scapula meet at the inferior angle, or tip, of the scapula.
The sternum, or breastbone, is a long, flat, bony plate that forms the most anterior section of the rib cage. It is extremely important that pressure is not exerted on the xiphoid process during chest compressions, as this can cause the xiphoid process to separate from the sternum, possibly puncturing the diaphragm or liver. Shahab Shahid MBBS Richard L. Drake, A. Wayne Vogl, Adam.
Legal. The xiphoid process functions as a vital attachment point for several major muscles. The lateral chest radiograph is a complementary radiographic projection that allows visualization of the retrocardiac left lower lobe and the retrodiaphragmatic lung bases, and it allows evaluation of the thoracic vertebrae.
7.4). The sternum is also known as the breastbone. Evaluation of both PA and lateral chest radiographs allows anatomic localization and characterization of thoracic abnormalities and the formulation of an appropriate differential diagnosis. Figure1.7.33.
CT is the best investigation for imaging the sternum because it eliminates overlapping structures, detects bony destruction, allows imaging of adjacent soft tissues (the parasternalinternal mammary zone) and has good contrast resolution superior to that of conventional radiography or tomography. The sternum can also be prevented from gliding by soft-tissue restriction or dysfunction of the sternoclavicular joints and costoclavicular joints on one or both sides.
Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. This website provides entertainment value only, not medical advice or nursing protocols. Fish and snakes lack a sternum, reptiles have a U-shaped pectoral girdle, and birds have a massive sternum for the attachment of powerful wing muscles. All content published on Kenhub is reviewed by medical and anatomy experts. Figure1.7.35. Similar condensations then appear and connect the anterior ends of ribs 810, which eventually fuse with that of the seventh rib above.  See Table 6-4 for structures associated with various regions of the thoracic cage. Our mission is to provide objective, science-based advice to help you make more informed choices. The clavicular notches for the articulation of clavicles are projected upward and laterally on both sides of jugular notch. 2022 You must consult your own medical professional. 6-2). The radial nerve follows this groove and helps define the distal attachment for the lateral and medial heads of the triceps. Innerbody Research does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. During development the sternum is comprised of four individual sections called sternebrae, which fuse to form the sternum in adulthood. [ "article:topic", "sternum", "license:ccbysa", "showtoc:no" ], https://med.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fmed.libretexts.org%2FBookshelves%2FAnatomy_and_Physiology%2FBook%253A_Anatomy_and_Physiology_(Boundless)%2F7%253A_Skeletal_System_-_Parts_of_the_Skeleton%2F7.4%253A_The_Thorax%2F7.4A%253A_Thoracic_Cage%253A_Sternum, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\), status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Describe the structure and function of the sternum. I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half. There are a few important landmarks on the manubrium. Enter your email address below and hit "Submit" to receive free email updates and nursing tips. The xiphoid process does not fully join the body of the sternum until adulthood. So the inter-chondral portion of the ribs is myostructurally different to the more lateral intercostal complex, and has a distinct innervation via the most ventral branches of the intercostal nerves. Various sternal deformities are described, and the most important radiologically is the depressed sternum (funnel chest, pectus excavatum) in which there is approximation of the lower half of the sternum and the spine (Fig. Last reviewed: July 19, 2022
See Table 6-4 for structures associated with various regions of the thoracic cage. Our mission is to provide objective, science-based advice to help you make more informed choices. The clavicular notches for the articulation of clavicles are projected upward and laterally on both sides of jugular notch. 2022 You must consult your own medical professional. 6-2). The radial nerve follows this groove and helps define the distal attachment for the lateral and medial heads of the triceps. Innerbody Research does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. During development the sternum is comprised of four individual sections called sternebrae, which fuse to form the sternum in adulthood. [ "article:topic", "sternum", "license:ccbysa", "showtoc:no" ], https://med.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fmed.libretexts.org%2FBookshelves%2FAnatomy_and_Physiology%2FBook%253A_Anatomy_and_Physiology_(Boundless)%2F7%253A_Skeletal_System_-_Parts_of_the_Skeleton%2F7.4%253A_The_Thorax%2F7.4A%253A_Thoracic_Cage%253A_Sternum, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\), status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Describe the structure and function of the sternum. I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half. There are a few important landmarks on the manubrium. Enter your email address below and hit "Submit" to receive free email updates and nursing tips. The xiphoid process does not fully join the body of the sternum until adulthood. So the inter-chondral portion of the ribs is myostructurally different to the more lateral intercostal complex, and has a distinct innervation via the most ventral branches of the intercostal nerves. Various sternal deformities are described, and the most important radiologically is the depressed sternum (funnel chest, pectus excavatum) in which there is approximation of the lower half of the sternum and the spine (Fig. Last reviewed: July 19, 2022
The bone covers and protects the heart and great vessels in part, as well as the trachea and esophagus.
The bone is divided into three parts: The sternum lies very superficially in the anterior thorax and is easily palpable below the skin of the chest in the midline.
The xiphoid process is a small projection of bone which is usually pointed.
the joints between the ventral extremity of ribs one to seven and the costal cartilages, that then link rib to sternum).
The radial (spiral) groove runs obliquely across the posterior surface of the humerus.
The coracoid process is the site of attachment for several muscles and ligaments of the shoulder complex.
Whenever you see the word process on a bone, its referring a projection coming off the bone. Blood supply to the sternum arises from the internal thoracicartery. The infiltrate, which is perivascular and lymphocytic, is usually sparse, but it was a little heavier in the case overlying the hip prosthesis.350, Nyree Griffin MD FRCR, Lee Alexander Grant BA (Oxon) FRCR, in Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology Essentials, 2013, A depressed sternum resulting in the anterior ribs projecting more anteriorly than the sternum (funnel chest) it may be an isolated abnormality or associated with other disorders such as Marfan's syndrome or congenital heart disease (particularly an ASD), The condition is best assessed on a lateral CXR PA CXR: leftward shift of the heart an indistinct right heart border simulating middle lobe disease (the sternum replaces aerated lung at the right heart border) a steep inferior slope of the anterior ribs undue clarity of the lower dorsal spine seen through the heart, Pigeon chest (pectus carinatum): the reverse deformity, which may be congenital or acquired, Efthymia Nikita, in Osteoarchaeology, 2017. Before delivering chest compressions, you need to locate the xiphoid process at the end of the sternum so that you can avoid putting pressure on it during chest compressions. A diagrammatic representation of the embryological development of the sternum. The lower border of the manubrium articulates with the body of the sternum at the sternal angle (of louis), it is where the second pair of costal cartilage attaches to the sternum and at the level of the inferior border of T4, is also clinically known as the Angle of Louis. The manubrium is the thickest portion of the sternum as it carries the greatest physical load.
Ribs 810 are known as false ribs because they articulate with the sternum indirectly, as their cartilage joins the cartilage of the seventh rib. From: A Comprehensive Guide to Geriatric Rehabilitation (Third Edition), 2014, Andreas Adam CBE, MB, BS(Hons), PhD, PhD (hon caus), DSc (hon caus), FRCP, FRCR, FRCS, FFRRCSI(Hon), FRANZCR(Hon), FACR(Hon), FMedSci, in Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology, 2021.
The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. This is well displayed in a lateral chest radiograph but is relatively inconspicuous in the frontal projection, in which only the manubrial margins are sometimes visible, giving rise to confusing shadows that may mimic mediastinal widening. Three-dimensional model of the thoracic cage. Join the nursing revolution. Bifurcation with a split into left and right branches at its inferior end. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster.
A variable number of bone growth centers emerge in the manubrium, the sternal body, and the xiphoid. They then fuse like a zipper in a rostral to caudal direction. 3.5). However, it was clearly shown by Chen (1952a, 1952b, 1953) in mice and Seno (1961) in chicks, that the sternum is in fact developed from the same lateral somatopleuric mesenchyme that gives rise to the pectoral muscles and so is fundamentally of appendicular rather than axial derivation. Clinically, the xiphoid process plays an important role as a bony anatomical landmark in the trunk and may be damaged by improperly administered CPR.
These parts are named after ancient words that refer to parts of a sword: The manubrium is the quadrangular-shaped portion that is located at the superior (upper) region of the sternum, resembling the knot part of a necktie. In this article, we will discuss the embryology, anatomy and clinical relevance of the sternum. Copyright 2022 RegisteredNurseRN.com.
The manubrium usually has one to three centers of ossification, whilst the two sternal bars fuse across the midline to form four units called sternebrae, each with one or two centers of ossification.
The medial or sternal end of the clavicle articulates with the manubrium of the sternum, forming the SC joint. Ribs 11 and 12 are called floating ribs because they do not articulate with the sternum at all. On each side of the jugular notch, we have the clavicular notches, which articulate with the sternal end of the clavicle bones to form the sternoclavicular joint.
All cases have shown variable but usually mild epidermal atrophy and capillary telangiectasia in the upper dermis.
The apex of the lung extends above the sternoclavicular joint and the clavicle.
Clinically the inferior angle is relatively easy to palpate and therefore can be useful in tracking scapular motion. Read more. Reticulate telangiectatic erythema is an asymptomatic telangiectatic and erythematous plaque that develops some time after the implantation of a device, usually a pacemaker or cardiac defibrillator.348,349 It has also been reported overlying a hip prosthesis.350 The cases reported as sternal erythema, a distinctive thoracic surgical wound eruption that developed after coronary bypass grafting,351 appear to be a related entity.352 So too are the erythematous patches, sometimes quite large, that develop on the breast following a surgical procedure.
Anterior view of the corpus sterni with xiphoid process. Other anatomic structures are present at the general level of this plane. Posterior surface gives rise to the inferior sternopericardial ligament. The sternum is a complex and variable bone. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. All Rights Reserved. The flattened lateral portioncalled the acromial endarticulates with the acromion of the scapula, forming the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. It protects vital organs, such as the heart and lungs, and facilitates breathing and blood cell production.
The sternum is the bone that lies in the anterior midline of our thorax. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), the xiphoid process may be used as a bony landmark to determine the location for administering chest compressions. Figure1.7.32.
and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide!
The proximal humerus (Fig. The fibres of rectus abdominis and aponeurosis of internal and external obliques are attached to its anterior surface. Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, Develops from a left and right cartilaginous plates that unite in the midline. This is the opposite of pectus excavatum, and occurs when the ribs and sternum grow abnormally, so the sternum protrudes outwards. The lower border is narrower, is quite rough, and articulates with the body with a thin layer of cartilage in between.