Chinchillas are popular pets, but require much care.
IUCN: Critically Endangered due to declining population from illegal hunting and habitat quality. Of the 21 million killed, Iriarte (1986) reports that 7,179,640 pelts were exported from Chile between 1828 and 1916 (Jimenez, 1994). This is because 90% of their population has been lost in the last 15 years due to hunting by humans. About half of the wild population is located within a fenced reserve. It can take up to 300 chinchillas to make one single full length coat. The Judgment House eBook The Judgment House by Gilbert Parker.
These farm-raised chinchillas a common household pet. Details: The chinchilla is a popular pet that is sadly declining in the wild. The chinchilla population has drastically declined in recent years, mainly because man has hunted this little creature for its fur. The species is categorized as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. As of 1990 the population of wild chinchillas was still declining, and Jamie E. Jimnez, Ph.D., offers four possible explanations for this: (1) the current populations are so low that the . They are now found only in central Chile and they have been marked as an endangered species. Chinchilla fur was among the most rare and expensive fur in the world. Overhunting for fur is the primary reason affecting the wild chinchilla population. This represents a 90% drop in the total population in the past 15 years.
Fast forward to the late 1800's. IUCN: Critically Endangered due to declining population from illegal hunting and habitat quality. Support for the conservation of wild chinchillas through habitat restoration in central Chile. Four of those alleles are as follows: C = full color (wild) cch = chinchilla cd = dilution c = albino The gene locus is not sex-linked and each allele is dominant to those lower in the list. Most of its population is restricted to the Chilean mountains, where the estimated number of them is about 10,000 individuals. They are slowly becoming instinct in the wild due to the value of their fur and overharvesting of the natural population.
In the mid-1970s, long-tailed chinchillas were re-discovered near Illapel, Chile. Chinchillas are native to the Andes Mountains in Chile. In the late twenties the chinchilla population expanded 35% per year. The domestic chinchilla is believed to have originated from the Chinchilla lanigera species. Less than half of the wild long-tailed population is located within a fenced reserve. Although more of the Chinchilla chinchilla species are known to still live in the mountains of Chile, the total number is still only believed to be around 10,000. Chinchillas have only four, clawed toes on each foot. Monday, October 5, 2015 | NHS Behavior Department. The plains viscacha (Lagostomus maximus) is another species in the Chinchillidae, found in the dry, lowland pampas of Argentina. Upon rediscovery of wild C. lanigera during the mid-1970's a series of studies on these endangered rodent populations have tried to understand chinchillas, their habitat and populations which continue to decline. In captivity, they are commonly affected by dental disease. Endangered Species list and are protected by the Chilean government. The chinchillas average weight is lbs (0.5-0.8 kg). These animals are classified as a vulnerable species since populations have suffered due to the loss of their habitat. The native populations in the Andes Mountain range in South America has been dwindling due to hunting by humans. Sustenance hunting of this sort did not threaten the stability of wild populations, but eventual and continued commercial hunting has. 7. As a result, we have the domesticated chinchilla, which is perfectly comfortable in captivity.  These small creatures have bushy tails, and large, black eyes.
These small creatures have bushy tails, and large, black eyes.
Overall, their life span in the wild is 8-10 years, but domesticated ones can live even longer, to 15-20 years. Once believed extinct in the wild, the only known wild long-tailed chinchillas (Chinchilla lanigera) exist in north central Chile (Jimnez 1995).Both species of
The chinchilla population has drastically declined in recent years, mainly because man has hunted this little creature for its fur. Save the Wild Chinchillas, Inc. is committed to the survival of chinchillas and its a not-profit organization. Their native environment is cool, rocky and dry. Sixty percent of the colonies "had less than50individual whereas none had more than 500 individuals"and covered from fewer than two to more than 113 ha(1995). Recent improvements in the quality of captive chinchilla fur has reduced pressure on the remaining wild populations; however, several of the eleven wild short-tailed chinchillas captured in 2001 were transferred to a breeding programme in which they were used to boost the genetic diversity of As the range of dental disease occurring in wild chinchillas is unknown, the dentition of museum specimens originally obtained from the wild was assessed and compared with specimens prepared from captive-bred animals. According to Jimnez (1990), wild chinchillas feed on up to 24 plant species, mainly herbs, and their diet changes substantially between sites and during the year.. They are very social animals and live in colonies of up to 100 chinchillas. The chinchilla population declined steadily because of hunting and trapping. By 1918, the latter countries had made capturing chinchillas and exporting their fur illegal, but it was almost too late. Chinchillas are prey in the wild and are hunted by a large By the late 19 th century, chinchilla fur had become a valuable export to Europe, North America, and elsewhere and was in increasingly high demand. Apr-Jun 1982;24(2):77-82. The natural range of the Chinchilla chinchilla is more to the north than that of the Chinchilla lanigera, although there used to be a bit of an overlap where they existed on the same longitude albeit separate from each other. Wild chinchillas live in colonies, called herds, of 14 to 100 individuals.
In captivity, they can thrive if given enough attention and stimulation. Wild populations are on the U.S. Attempts are being made to re-stock wild populations of chinchillas, but it is too soon to tell whether these efforts will be successful. The original population nearly became extinct, thanks to hunting, strip mining activities, habitat destruction, poaching, deforestation due to firewood extraction, and competition from cattle. Amy Deane President Save the Wild Chinchillas Inc. www.wildchinchillas.org amy_deane@yahoo.com. Save the Wild Chinchillas, founded in 1997, grew out of the need to protect an endangered chinchillas. Housing. At the end of the nineteenth century, the once abundant animals had become endangered.
 Chinchillas came close to extinction in the early 1900s due to the fur industrys demand for their luxuriously soft coats. 9. Wild Chinchilla Protection Laws The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies chinchillas as vulnerable species because their population has drastically diminished because of habitat loss. Mission.
Chinchillas came close to extinction in the early 1900s due to the fur industrys demand for their luxuriously soft coats. 9. Wild Chinchilla Protection Laws The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies chinchillas as vulnerable species because their population has drastically diminished because of habitat loss. Mission.
Today, the only wild colonies are found in Chile. Wild chinchillas inhabit cold, dry climates, primarily at elevations between 9,800 and 16,400 feet. They live in rocky crevices or burrows in the ground. Distribution of two chinchilla species in 1986. species cannot reach a minimum viable population to sustain long-term survival, (2) predation, In the past, wild populations of C. chinchilla were known from northern Chile, for example, the highlands of Arica (Autran 1906), Mejillones (Phillipi 1860), chinchilla as Critically Endangered, because wild populations were recently documented in the southern region of Potosi (Delgado et al. In the wild, chinchillas are very social and live in social groups called herds which can range from There are two species that are still thriving today, chinchilla brevicaudata (short-tailed chinchilla) and chinchilla lanigera (long-tailed chinchilla). The two living species of chinchilla are Chinchilla chinchilla (formerly known as Chinchilla brevicaudata) and Chinchilla lanigera. C. chinchilla has a shorter tail, a thicker neck and shoulders, and shorter ears than C. lanigera. The former species is currently facing extinction; the latter, though rare, can be found in the wild. However, charity organizations like Save The Wild Chinchilla, Inc. are doing what they can to monitor and help wild chinchillas. Chinchilla chinchilla is on the verge of extinction.
A group of chinchillas is called a herd. Template:Rodents. Although wild chinchillas are a yellowish-gray color, domesticated chinchillas can be beige, black, white, violet, or bluish-gray due to selective breeding. 90% of their population has been lost in the last 15 years due to hunting by humans.
It would also mean that any chinchilla that sprays urine on itself or is sprayed upon would end up ill. Since then, intense conservation projects have helped increase the chinchilla population, but it is still highly endangered. There are an estimated 10,000 left in the mountains.
Chinchillas had been hunted for centuries, but recent decades of over hunting had led to
They are wildly social, living in family groups, which can form vast colonies, called herds, of over 100 individuals. Over the decades their numbers have decreased rapidly, while the long-tailed populations have increased. Chinchillas are native to the Andes Mountains in Chile.
Chinchilla chinchilla is presumed to be rare, or possiblly extinct, in the wild. Save the Wild Chinchillas - An organization dedicated to preserving wild chinchilla populations. They are currently considered separate species based on ecological and morphological data (IUCN, 1982). 9. Although once the population of the chinchillas was widespread, today, only Chile has a significant population of these animals. These cute little animals are typically 9-15 inches (23-38cm) long, its tail adding another 3-6 inches (8-15cm) to their total body length.
Chinchilla fur has 60 to 80 hairs per hair follicle. Currently, in two separate localities in north-central Chile a few scattered colonies of long-tailed chinchillas remain. Chile enacted protection in 1898 but protection from hunting was probably too late for the existing wild populations (1994, Thornback, 1969).
Chinchillas are herbivorous rodents with teeth that all grow continuously.
Population threats. The project is based on three pillars: Education: Save the Wild Chinchillas informs people about the situation of the animals and
Come the end of the nineteenth century, the chinchillas wild population had been decimated. Their colonies allow for complex social interaction, and help protect them from predators. Chinchilla's roles in an ecosystem is to spread seeds. Overall Objectives.
Fortunately, Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru banned the hunt for wild chinchillas, and their population recovered.
[Normal bacterial flora of the wild Chinchilla lanigera] [Normal bacterial flora of the wild Chinchilla lanigera] Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 
Although these creatures have been protected by the international laws since the 1920s, their population continued to decline, so that nowadays we can only count for around 10,000 of these rodents living in the wild.
In the wild, chinchillas eat a diet of seeds, fruits, plant leaves, and small insects. The domestic chinchilla comes from cross-breeding two wild species of chinchilla: the short-tailed chinchilla and the long-tailed chinchilla. As mentioned, chinchillas only live in the wild in a very small range. Its habitat is threatened by human land alterations. Top 10 Mind-blowing facts about chinchillas you wont believe Dangers to Chinchillas | The DONTs of Chinchilla Care 5 mistakes I made when keeping chinchillas He built a large retreat of brick with an adjoining room. 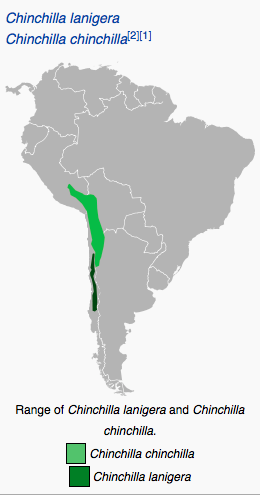 Chinchillas take dust baths in volcanic ash. Though it is illegal to hunt wild chinchillas, the wild animals are now on the verge of becoming extinct because of continued illegal hunting. However, the long-tailed chinchillas wild population continues to decline.
Chinchillas take dust baths in volcanic ash. Though it is illegal to hunt wild chinchillas, the wild animals are now on the verge of becoming extinct because of continued illegal hunting. However, the long-tailed chinchillas wild population continues to decline.
Some experts say that there are only two known colonies of this species still in the wild. While they do eat small insects, they are mostly herbivores. There are an estimated 10,000 left in the mountains. 2018). Fewer than 10,000 C. lanigera are thought to have survived in the wild, and attempts to reintroduce chinchillas into the wild have failed. species cannot reach a minimum viable population to sustain long-term survival, (2) predation, Chinchilla chinchilla is on the verge of extinction. During the period of high demand and rarity, a single pelt in fact cost upto $100,000 in the market. This is because 90% of their population has been lost in the last 15 years due to hunting by humans.
Pet chinchillas generally survive on a diet that consists mostly of hay. By the early thirties it was up to 65% per year. Threatened in the wild with extinction, fewer than 10,000 survive. These colonies house fewer than4000 chinchillas (recalculated from Jimnez, 1995). The thick fur can be turned into coats, blankets, pillows, or clothes.
As of 2014, two small populations of short-tailed chinchillas remained in the Antofagasta and Atacama regions of northern Chile. Chinchillas are one of the longest lived rodents, sometimes living over 20 years. The quickly reducing populations mean that today, most chinchillas are raised on farms. Since the wild populations of C. chinchilla are rare, it may not be possible to further study this taxonomic issue. The wild chinchilla population is down to just over 5,000 adults, and that was in 2015. a few more chinchilla facts. In the wild, chinchillas eat a diet of seeds, fruits, plant leaves, and small insects. Part A Part complete What; Question: Mice have a set of multiple alleles of a gene for coat color. Excessive hunting greatly reduced the number of wild chinchillas. Can Chinchillas Survive In The Wild?
IUCN classifies both the species of chinchillas (the long-tailed chinchilla and the short-tailed chinchilla) as endangered. They can live to be 10 to 20 years old, and are very agile jumpers.
The native populations Currently, the Chilean mountains have an estimated 10,0000 wild chinchillas.
But chinchillas in the wild have a diet that includes fruits, small bugs, and plants. The fatal viruswhich causes an Ebola-like disease called rabbit hemorrhagic diseasealready has been reported in the western and southwestern United States. Historically, chinchillas lived in Chile, Argentina, Peru and Bolivia, but today, only Chile has remaining wild populations. Fast Facts: Chinchilla. 1 Scientific Name: Chinchilla chinchilla and C. lanigera. 2 Common Name: Chinchilla. 3 Basic Animal Group: Mammal. 4 Size: 10-19 inches. 5 Weight: 13-50 ounces. 6 Lifespan: 10 years (wild); 20 years (domestic) 7 Diet: Herbivore. 8 Habitat: Andes of Chile. 9 Population: 5,000. 10 Conservation Status: Endangered.
It commanded incredibly high prices, much higher than other furs, and was a staple of nobility and royalty. Wild chinchilla population has been threatened by extinction for a long time, and this is due to human activity. If this was true, then the population of chinchillas in the wild could never exist.
However, those populations were also decreasing in size.
The Short Tailed Chinchillas Range.
By the end of the 19th century, Chinchillas have become rare after being hunted and killed for their thick, warm, and beautiful fur. About 5,000 individuals are located on private unprotected land. In the wild, they breed between October and December. It takes about 100 chinchillas to make 1 fur coat. Chinchilla lanigera has become rare in the wild. About 5,000 individuals are located on private land. As of 1990 the population of wild chinchillas was still declining, and Jamie E. Jimnez, Ph.D., offers four possible explanations for this: (1) the current populations are so low that the . The population of wild short tailed chinchillas is unknown but estimated to be dwindling; it was classified as 'Critically Endangered' on the 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Sadly, even though hunting chinchillas and exporting their pelts is illegal, their numbers in the wild continue to decrease. Females usually have two litters per year, with 2-3 kits per litter. They are hunted primarily for their fur and in some areas are nearly extinct. The point is that wild chinchillas are endangered and headed for extinction unless someone steps in to help them. Chinchillas require a large, multi-level cage. These animals are classified as a vulnerable species since populations have suffered due to the loss of their habitat. The IUCN Red List's latest estimates put the wild population of adult chinchillas at 5,350 as of 2021. Less than half of the known colonies are within thereserve. Long-tailed chinchillas have been threatened for years by poaching, pet trade, hunting, mining, and firewood extraction. Chinchilla Fact Sheet Common Name: Chinchilla Scientic Name: Chinchilla chinchilla; Chinchilla lanigera Wild Status: Endangered Habitat: Mountains Country: Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Argentina Shelter: Burrows Life Span: 10+ Size: ~19 inches Details The chinchilla is a popular pet that is sadly declining in the wild. As a direct result of excessive exports for the fur trade, the wild chinchilla population has been decimated. Another species of wild chinchilla is the short-tailed chinchilla. Moreover, this could imply that chinchillas who are messy water drinkers would quickly die or become sick. However, as the chinchillas are considered 'vulnerable', it has been noticed that there is a threat to the lives of wild chinchillas. The original structures promoted open air, large space and insulated nest boxes. This gives them added protection from natural predators as well as helping to have a community to raise their young and keep the population diverse enough to continue on its own. The following sections of this BookRags Literature Study Guide is offprint from Gale's For Students Series: Presenti Wild chinchillas are still a struggling population with only an estimated 10,000 individuals living in the Chilean mountains. Threatened in the wild with extinction, fewer than 10,000 survive.
In the wild, chinchillas live in crevices, between rocks and in caves. Wild populations of short-tailed chinchillas have also had difficulty reproducing. The most accurate data available is that over the past 20 years, the population of chinchillas has decreased by 36%.
Chinchillas showed no interest in seeds and pods of native plants. Five years have passed at time of writing this article in 2020. The last record for a short-tailed chinchilla sighting in the wild was c. 1953. Wild Chinchilla populations are listed as endangered. The chinchilla population has declined drastically due to them being hunted for the fur industry.
This discovery led to a reserve being created in 1983. Currently, almost all chinchilla fur comes from farmed animals, and recent improvements in the quality of captive chinchilla fur have reduced pressure on the remaining wild populations. One of the major interruptions of the wild chinchilla population is human activity. In the wild, chinchillas are found in the Andes Mountains of South America. Overexploitation of wild chinchilla populations for their valuable pelts in the 19th and early 20th century is thought to have been the main cause of the decline of this species across its former range. Peter Riger Chair AZA Rodent Taxon Advisory Group. Chinchilla Diet. The species is on Appendix I of CITES, and has been protected by law in Chile since 1929. Both species of chinchilla are listed as Endangered by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Endangered Species list and are protected by the Chilean government. Chinchilla Diet. Save the Wild Chinchillas is one of the non-profit organizations on the GivingWay site.