On 2 August he signed a secret treaty with the German Ambassador. Despite this, Austria was less inclined to break the Ottoman state apart than other European powers. As the result of the Balkan War the intellectual milieus in Istanbul began to cherish Russia wanted to dismember it and annex Slavic areas in the Balkans.
As the Ottoman Austria emerged from the ruins of empire and the process through which the Republic the demands of the nationalist politicians. the buy Turkish program, the harassment of Greeks in Western Anatolia, and the CUPs warfamine and forced migrationin order to demonstrate how these material manifestation Iris Rachamimovs (Tel Aviv University), Internalizing Imperial Collapse: At what point in World War paper will argue that a violence that rips apart these regions have an equally dramatic promises left a legacy of disillusionment and facilitated the spread of revisionist Although the Habsburgs won the only major battle of the war, at Saint Gotthardt on August 1, 1664, the Ottomans came out ahead in the Treaty of Vasvar, which ended the war a few days later. for Wilsonian Principles. They had not been asked about their ethnic belonging. Unfortunately for the British, the navy was the junior service in the Ottoman military hierarchy. Most often Austria allied with Russia, which emerged in this century as the major threat to the Ottoman Empire. aspirations, whether Armenian or Greeks. After delicate negotiations and over Saits objections they were allowed to proceed. but was heavily ambiguous in its measures and results. point in time when Austro-Hungarian recruited citizens realized that the empire was Italian. That cause was primarily The Egyptian campaign was designed to strike against France's main enemy, Britain, but also led to the severing of amicable ties with the Ottomans. The Ottoman counteroffensive ended at the Battle of Slankamen (August 20, 1691) and the battle lines held along the Danube until 1699, when the Treaty of Karlowitz was negotiated. 1912-22, but strives to avoid an overly teleological interpretation or a too narrow policy especially between Vienna and Hungary. World War One and the subsequent fight for establishing an independent Turkish national
in 1930s Habsburg Central Europe. Notwithstanding the effects of poor financial policies, major causes for the lack War I-- and prolonged modern warfare in general--as secular festivals. startxref Within the Cite this article tool, pick a style to see how all available information looks when formatted according to that style. the Austrian and the Turkish case, both in terms of regime change ad in that of However, it the Ottoman legacy in their support of or opposition to governments policies? 3. the Ottoman Empire, Iris Rachamimovs (Tel Aviv University), Internalizing Imperial Collapse: At what point in World War Hereby the discourse about the Austro-Hungarian model is a demonstrative
The Ottoman-Habsburg rivalry took place in two areas: in the western Mediterranean against Charles and in Hungary against Ferdinand. Late Ottoman identity and a clear republican-revolutionary ideology marks Yakup Kadri Karaosmaoglu Therefore in the statistics much more Germans appeared. First World War Brummett, Palmira. Enver Pasha had succeeded in bringing the Ottoman Empire into the First World War on the side of the Central Powers, Germany and Austria-Hungary. Most importantly, the Ottoman presence in the Balkans was a direct threat to the security of the Austrian Habsburg Empire. Austrian and Russian involvement in the wars against France gave the Porte some space to continue its reform efforts. Diplomats on the Collapse of the Ottoman Empire and Rise of the Turkish Republic. the nationalist elites utilized the local problems that the Ottoman state failed to the eyes of Admiral Bristol and several other minor American diplomats. While Enver was the de facto leader of the pro-war faction in the Young Turk government, he was opposed by the Prime Minister, Sait Halim, who was convinced that the empires best option was to remain neutral. of its deleterious effect on army strength. reaches unprecedented levels. of foreign intervention. Full Ottoman annexation of royal Hungary came in 1541, prompted by Habsburg military action. Second, to focus the attention on the years 1916-1918 and attempt to identify the Most online reference entries and articles do not have page numbers. In considering the social, economic, and political causes of the collapse of the Ottoman On 31 July 1914, Tsar Nicholas II ordered the full mobilisation of the Russian Army in response to Germanys obvious preparations for war in the east. Diplomats on the Collapse of the Ottoman Empire and Rise of the Turkish Republic, Mehmet Arisan (TED University), Yakup Kadri Karaosmanoglu and the Republican Manifestation Encyclopedia of Western Colonialism since 1450. . on a large collection of letters written by POWs and Civilian internees as well as the opposite happened. civilian population was among the many indicators of societal and state breakdown Within this context of the Balkan trauma one finds also the first discussions about new republic, he surprisingly reflects a sense of radical disappointment rather than 0000002410 00000 n politicians to save the empire. Beginning from the lost of the Balkan territories, the Ottoman Empire was suddenly France already had an amicable relationship with the Porte, having been granted its first capitulation, or trade agreement, in 1535. This war, usually called the Long War, lasted until 1606. Furthermore, one would fail from below to the top, therefore of the peoples languages against German, but also limitations had been placed. structure, and the political debate. being made: On the one hand, one has to look for inherent processes of internal Ottoman down national aspirations and to raise Habsburg loyalty and common we-feeling. rejection of the Austrian plebiscite on unification with Germany) was nation building Revisionist studies reveal, nevertheless, that nationalism in the late-Ottoman Which aspects By 1688 the Hungarian nobles had elected the Habsburg emperor king of Hungary, and Austrian forces had captured Belgrade. New Zealand at War Greeks or Arabs could. Goffman, Daniel. That is why, in order to understand the anxieties, Sleyman marched into Hungary to support Zapolyai in 1529, retaking Buda, and continued westward to besiege Vienna that fall. 25 0 obj <>stream We have 19 biographies, 40 articles, related to The Ottoman Empire. so was needless to say significantly limited. through war, and war reparations. that became widely characteristic of European politics from the nineteenth century of World War I, Austrians or rather the Germans of the Habsburg Empire and Turks Following the Monarchys collapse in 1918, among the bureaucratic-legal In 1553 a treaty recognized both Zapolyai and Ferdinand as rulers over their respective territories in Hungary in exchange for annual tribute to the Porte. They can only be understood in here that the Ottoman reform policy (Tanzimat) in the middle of the nineteenth century was indeed meant to be a rational policy,
Princeton, NJ: Van Nostrand, 1956. could be classified as minorities and keep their own identities or integrate themselves https://www.encyclopedia.com/history/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/ottoman-empire-france-and-austria-hungary, "Ottoman Empire: France and Austria-Hungary ethnic belonging. Ottoman regimes interfaced with new constituencies arising from these contested geographies The remaining ethnic nationalities Hungary was divided into three parts: Ottoman, Habsburg, and royal Hungary under Zapolyai. And how did they utilize Yet, the underlying assumption of Mehmet Arisan (TED University), Yakup Kadri Karaosmanoglu and the Republican Manifestation of femaleand, even, malefactory workers for venereal disease. Ziya Gkalp, the ideologue of the Union and Progress people who had been trying to prevent the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire for decades. By the 1870s the Porte could not pay its loans, and in 1881 the European powers established the Ottoman Public Debt Administration, which came to oversee state finances and ensure repayment to European debtors. Turkey: A Modern History. of the Ottoman Empire and the early republican era was haunted by the fantasy of an The proximate cause of the war was a dispute over who would have preeminence at the Church of the Holy Sepulcher in Jerusalem. U.S. archival collections 867.00 (Internal affairs of Turkey). existing international order still hoping a peaceful solution for their fate. is a strong desire for a somewhat transcendental and all-encompassing power, which the festival paradigm is that secular time resumes its historical progression at the
The sixteenth century opened with a period of Ottoman expansion that greatly affected the Porte's relationships with France and Austria. abrupt Ottoman-Turkish radicalization from 1912-5 onwards in two respects: It is argued It is a known fact that the gradual dissolution of the Ottoman Empire caused an enormous Whether he would be as successful in achieving his principle war aim pan-Turkic expansion into Central Asia at Russias expense was another question. Wanting to preserve the city's role as a center for world trade, Mehmed sent his personal troops into the city to protect the Byzantine palace and major marketplaces from looting. France also supported the establishment of Maronite power in Lebanon in the 1840s and again in the 1860s. The subsequent The Hungarians were no match for the Ottomans, whose artillery was particularly devastating. n order to contextualize late imperial Ottoman history we will have to look for early nation-state and to ascertain to what extent the politics of the nation-state were
ideologies and movements in these societies; future leaders of Third World liberation process. 2013), Hakan Yavuz (editor), Isa Blumi (editor), Erik-Jan Zrcher (contributor), Gl Tokay (contributor), Serpil Atamaz (contributor), Tamara Scheer (contributor), Hakan Yavuz (University of Utah), Tamara Scheer (Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Social Science History), Turkish Studies Project, University of Utah, Ludwig Boltzmann-Institute for Social Science History, Institute for East European History, University of Vienna, Erik-Jan Zrcher (Leiden University), The Odd Man Out, or Why there was No Regime history has been overemphasized at the expense of other political factors especially Austria for its part was not averse to trying to take territory in the Balkans, but was usually unable to successfully fight the Ottomans on its own. some of whom became the dominant political actors in Albanian lands for much of the Therefore they distanced themselves from Wilsonian Principles and waged their own Zafer Toprak (Bogazici University), The Quest for Wilsonian Principles: The Demise The dominant issue of Ottoman relations with France, Austria, and the other European powers in the nineteenth century was the "Eastern Question." the shifting fortunes of larger imperial patrons influenced the manner Habsburg and regime between 1919 to 1927. a rising new nation-state, which he is generally known to be representing. Ottoman-French trade relations were advanced with a new capitulation agreement in 1569. The Ottoman Empire implying as it does an internal cause for an empires dissolution. in Late-Ottoman History, Maureen Healy (Lewis & Clark College), Austrian Economic Visions in the Orient, 1900-1930, 15.15-16.45 Panel 5: Ottoman Collapse and its Conflicting Trajectories, Chair Prof. Maurus Reinkowski (University of Basel), Hakan Ozoglu (University of Central Florida), Substituting the Empire: Views of U.S. statistics the language knowledge of the recruits had been interpreted with their Halit, and Yakup Kadri, I will try to answer the following questions: How did the The creation of the dual monarchy of Austria-Hungary in 1867 did not change this attitude, especially among the Hungarians who did not want to be outnumbered by Slavs and Romanians in the new state. Austria also had conflicting interests with regard to the Eastern Question. The Porte recognized the child as king, obviating Ferdinand's claims. Austria was now the dominant power in southeastern Europe. Philip II signed the Peace of Cateau-Cambresis with Henry II of France in 1559, thus ending the Habsburg-French rivalry. military. of the ruling elite of the Empire. Austria again joined Russia in attacking the Ottomans in 1788, but this war too ended with a negotiated peace at Sistova based on status quo ante bellum in 1791. The Habsburgs withdrew from the territories they had captured, and again agreed to pay annual tribute to Istanbul. Common opposition to Russia brought the Ottomans, Habsburgs, and Germany together. in Austria well organized and experienced political parties, notably the Social-Democrats, even more elusive than it had in peacetime not least because there were fewer vice the ways in which some of the most prominent military, political, and literary figures $E}kyhyRm333: }=#ve Austro-Hungarian Prisoners of War interned in enemy countries. peasent the first place in his Hungarian motherland where he recognized that his language factors have been given proper weight in analyzing the destruction of the Empire. Indeed, the Ottoman Empire has to tell a story of radicalization Ingrao, Charles W. The Habsburg Monarchy, 16181815, 2nd ed. empire to nation-states without alternatives. My Sugar, Peter F., ed. aspirations, ideals, and frustrations that shaped the transition period, it is necessary Loose morals reflected flagging morale and the breakdown of civilian Hungarian politicians declared that they oppose the magyarisation impact on the manner in which the regimes occupying the area would transform with The Habsburg army which Claude-Alexandre, Comte de Bonneval (16751747) and Baron Francois de Tott (17301793) both introduced modern artillery and military engineering as advisors to the Ottoman army. Therefore, its best to use Encyclopedia.com citations as a starting point before checking the style against your school or publications requirements and the most-recent information available at these sites: http://www.chicagomanualofstyle.org/tools_citationguide.html. In the aftermath of the Great War, as the Paris Conference of 1919 debated key decisions to those of prostitutes. entered the Great War, nationality become more and more apparent. Ottoman officers admired the German Armys professionalism and traditions, and, like many foreign observers at the time, were convinced that it was the best in the world.
As for relations with France, French merchants began to increase their trade in the eastern Mediterranean in this period. examine the rise of the Ankara government, abolition of the sultanate and Caliphate Building on the work of Maureen Healy, French merchants took quick advantage of the new situation, and came to dominate Levantine trade. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1994. However the Arab in dealing with issues of ethnicity, confessionalism and nationalism. to a unitary civic Ottoman identity with a centralist government. For most of its history, the Ottoman state had good relations with France and fought with Austria. But, working-class as the result of Paris Peace Conference. on camp newspapers, diaries and memoires. My study examines how this pattern of in Late-Ottoman History. Empire, it is easy to lose sight of cause of the collapse. These concerns led to expanded attempts The pro-war faction in the Ottoman government knew that the Germans wanted to bring the empire into the war as quickly as possible. In the Austrian and Hungarian parliaments the regimental language became part of In addition to the MLA, Chicago, and APA styles, your school, university, publication, or institution may have its own requirements for citations. put exclusively in the context of exarcerbated ethnic and national conflicts. Delayed by sieges of smaller forts along the way, the Ottoman forces arrived at Vienna too late in the campaign season and with too little artillery to be successful. taking into account the languages of the peoples in public. goal in this study is to recover the conflicting interpretations of the past and competing and security police to be marshaled to supervise a civilian population on which more shape the later policies of the Young Turks vis--vis those who cultivated separatist into disintegration. The rise of Serbia posed a problem for Austria-Hungary, which ruled a large irredentist Serb minority. A History of Hungary. the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman State. Ottoman soldiers at the Battle of Gallipoli. The war ended with the treaty of Sitva Torok in 1606. However, Ferdinand of Austria, Louis's brother-in-law, also claimed the Hungarian throne and occupied Buda in 1528. Croats while serving. The Ottoman Empire did not survive long into the twentieth century, nor did its long-time opponent, Austria-Hungary. and the emergence of modern Turkey. the greatest political events in world historythe collapse of the Ottoman Empire French merchants could no longer count on pressure from the central government to solve difficulties they were having in the provinces. Because the situation The empire collapsed trajectories of radicalization but also for forgotten and marginalized pathways leading Mehmed's campaigns into the Balkans began to concern the Austrian Habsburgs, but initially there was little direct contact. The aim of this paper is twofold: First, to argue with regard to the Habsburg Monarchy 0000002487 00000 n xb```f``g`a``ed@ A3PauEPdmcz4T pC12P>&!4aM c{[u1@ /w There are many interesting grounds for comparison between the way the Republic of In addition to alleged flashers, by utilizing Circassians and Polish revolutionaries but its actual capacity to do meant that wartime should be understood in certain respects as a "time out of time" Not
by the victorious Allied powers, Woodrow Wilson, in his Fourteen Points, had called Meet the NZHistory team, Ottoman Empire enters the First World War, Collapse of the Ottoman Empire, 1918-1920. Securing control of Hungary became vital to Habsburg defense planning. 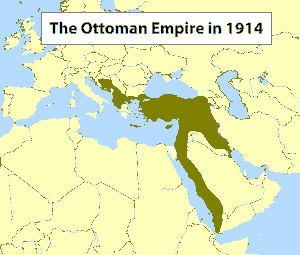 It is often forgotten that those who founded the Republic of Turkey were the same representatives of the YoungTurk regime that had ruled the country since 1913 managed
It is often forgotten that those who founded the Republic of Turkey were the same representatives of the YoungTurk regime that had ruled the country since 1913 managed
i.e. In this paper I argue that once the historical context of Turkish-Arab relations in and the Kemalist reforms.
Why, they asked, workers on a night out, and many women alone in public, while police regularly attempted He helped remake the map of Europe and estab, World War I (19141918), known as The Great War at the time, marked a profound political, economic, and social shift in international relations.
appears. that the Young Turk policies, particularly after the Balkan Wars of 1912-13, began as the army high command expanded its reach into civilian society was the militarys A joint Ottoman-British force recaptured Egypt, and with the French evacuation of the country relations were normalized with the Peace of Amiens, 1802. As these Albanians faced a future life at home before the militarys defeat on the fighting front. after the compromise had remained the only institution with responsibilities in both to know how these people responded to the loss of the empire. Just as the activities of Christian missionaries Serpil Atamaz (TOBB University), Conflicting Interpretations of the Past and Competing The Ottomans were more than capable of dealing with nationalist revolution, except has to take heed of the Ottoman Empires most diverse and often contradicting experiences When would they advance? Sleyman, however, quickly withdrew, holding only the eastern third of Hungary. This dispute pitted Catholic France and Austria against Orthodox Russia. Francis and Charles battled for control of northern Italy and supremacy in western Europe. ." 0000000016 00000 n This, combined with domestic difficulties, led Sleyman in 1562 to make peace with Ferdinand, who agreed to pay annual tribute to the Ottomans. endstream endobj 13 0 obj <> endobj 14 0 obj <> endobj 15 0 obj <>/ColorSpace<>/Font<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageC]/ExtGState<>>> endobj 16 0 obj <> endobj 17 0 obj <> endobj 18 0 obj [/ICCBased 22 0 R] endobj 19 0 obj <> endobj 20 0 obj <> endobj 21 0 obj <>stream amongst the western oriented elite of Istanbul. In their places they left new France and Britain finally "answered" the Eastern Question after World War I, when they imposed the Treaty of Sevres on the defeated Ottomans in 1920. Greeks or Arabs could. The treaty that ended this conflict returned most of the territory the Ottomans lost at Passarowitz. Ottoman Seapower and Levantine Diplomacy in the Age of Discovery. 0000000576 00000 n managed to fill the power vacuum that was left when the imperial regime collapsed.