Mol Endocrinol. In mammals, the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) express a robust rhythm of electrophysiological activity that controls the secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland, with the diurnal variation in melatonin being crucial for synchronizing the circadian rhythm (31).
 Brice NL, Varadi A, Ashcroft SJH, Molnar E. Metabotropic glutamate and GABAB receptors contribute to the modulation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic -cells. endstream
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212870110, 50. Apart from the paracrine feedback system, -cells have a glucagon autocrine feedback loop. Although the discovery of autocrine and paracrine interactions was initially overshadowed by the characterization of endocrine glands, the concept of cells being able to secrete regulatory factors was first appreciated more than 200 years ago by leading scientists of the time, including Brown-Squard whom many regarded as the father of endocrinology. It is now firmly established that the endocrine glands are regulated by a plethora of internal and external signals via blood circulation, and that these input signals can further trigger the release of autocrine/paracrine messengers. Flodgren E, Olde B, Meidute-Abaraviciene S, Winzell MS, Ahrn B, Salehi A. GPR40 is expressed in glucagon producing cells and affects glucagon secretion. Our Moosmosis site is run 100% by volunteers from around the world. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211495200, 29. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), another incretin hormone which acts on the Gs-coupled GIP receptor (GIPR), mediates similar responses as GLP1 but its mechanism of action is less understood (12). An example of autocrine and paracrine interaction between the NPY neuron, the POMC neuron, and their downstream effector neuron is shown in Figure 3. (2006) 147:39954006. Diabetologia. Schith HB, Fredriksson R. The GRAFS classification system of G protein-coupled receptors in comparative perspective. To adjust energy fluctuation caused by food intake, circadian rhythm or physical activities, the islet is sensitive to signals which are regulated by the hypothalamus as well as to other circulatory signals such as nutrients and hormones. Subtype-selective expression of the five somatostatin receptors. xSMo0Q*ZUe Ramracheya RD, Muller DS, Squires PE, Brereton H, Sugden D, Huang GC, et al. This makes sense because we only want blood clotting factors to heal a cut at the local site and not travel to other sites in the body that dont need it. J Biol Chem.
Brice NL, Varadi A, Ashcroft SJH, Molnar E. Metabotropic glutamate and GABAB receptors contribute to the modulation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic -cells. endstream
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212870110, 50. Apart from the paracrine feedback system, -cells have a glucagon autocrine feedback loop. Although the discovery of autocrine and paracrine interactions was initially overshadowed by the characterization of endocrine glands, the concept of cells being able to secrete regulatory factors was first appreciated more than 200 years ago by leading scientists of the time, including Brown-Squard whom many regarded as the father of endocrinology. It is now firmly established that the endocrine glands are regulated by a plethora of internal and external signals via blood circulation, and that these input signals can further trigger the release of autocrine/paracrine messengers. Flodgren E, Olde B, Meidute-Abaraviciene S, Winzell MS, Ahrn B, Salehi A. GPR40 is expressed in glucagon producing cells and affects glucagon secretion. Our Moosmosis site is run 100% by volunteers from around the world. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211495200, 29. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), another incretin hormone which acts on the Gs-coupled GIP receptor (GIPR), mediates similar responses as GLP1 but its mechanism of action is less understood (12). An example of autocrine and paracrine interaction between the NPY neuron, the POMC neuron, and their downstream effector neuron is shown in Figure 3. (2006) 147:39954006. Diabetologia. Schith HB, Fredriksson R. The GRAFS classification system of G protein-coupled receptors in comparative perspective. To adjust energy fluctuation caused by food intake, circadian rhythm or physical activities, the islet is sensitive to signals which are regulated by the hypothalamus as well as to other circulatory signals such as nutrients and hormones. Subtype-selective expression of the five somatostatin receptors. xSMo0Q*ZUe Ramracheya RD, Muller DS, Squires PE, Brereton H, Sugden D, Huang GC, et al. This makes sense because we only want blood clotting factors to heal a cut at the local site and not travel to other sites in the body that dont need it. J Biol Chem. Ghrelin-mediated appetite regulation in the central nervous system. The melanocortin receptors: lessons from knockout models. However, the Gq/11 transduction mechanism in regulating pancreatic hormone secretion remains to be fully elucidated.
63. Cooke D, Bloom S. The obesity pipeline: current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs. J Clin Invest. Likewise, the ablation of GCGR delays -cell differentiation and perturbs the proportion of - to -cells in embryonic islets, inhibits the progression of -cells to maturity in adult mice, as well as affecting the expression of several -cell-specific genes (90). The cells must be identical adjacent signaling cells, and each cell receive a strong autocrine signal, which amplifies the signaling. (NPY) receptor ligands. J Pineal Res. Gelling RW, Du XQ, Dichmann DS, Rmer J, Huang H, Cui L, et al. Acuna-Goycolea C, van den Pol AN. Gastroenterology. By activating phospholipase C (PLC) via Gq/11 protein, GHSR1a triggers the release of neuropeptide Y (NPY) that exerts paracrine effects (which will be discussed later). (|[@%)dQ:~82gT>u-zDQ8#{`'FjizY Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications. While exocrine cells constitute the major biomass of the pancreas, a small cluster of endocrine cells forms the pancreatic islet, including three key cell types: glucagon-secreting -cells, insulin-secreting -cells, somatostatin-secreting -cells (8) (Figure 2). doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0270133, 22. The inhibition of POMC together with the secretion of MCH and hypocretin/orexin appears to increase food intake and reduce metabolic rate by acting on the PVN of hypothalamus. Regulation of testicular function in the Stallion: an intricate network of endocrine, paracrine and autocrine systems.
Pancreatic -cell overexpression of the glucagon receptor gene results in enhanced -cell function and mass. Anim Reprod Sci. (2012) 109:190038. Perfetti R, Hui H, Chamie K, Binder S, Seibert M, McLenithan J, et al. The Y1R expressed in the ARC has been suggested to mediate the hyperphagic effect of NPY (60), while the ARC NPY expression is negatively regulated in an autocrine manner via presynaptic Y2R and Y4R present in NPY neurons (62, 63). For example, MC3R in ARC can bind MSHs as well as AgRP with the former acting as agonists and the latter as an antagonist. Hope you liked our educational post, everyone! doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800770, 5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.382473, 75. Morton GJ, Cummings DE, Baskin DG, Barsh GS, Schwartz MW. In terms of location: Autocrine is self.
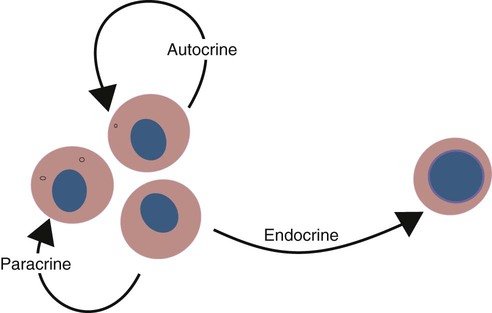
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00593.x, 34. Santulli G, Lombardi A, Sorriento D, Anastasio A, Del Giudice C, Formisano P, et al. <> Although the receptor for CART remains to be characterized, the activation of Gi/o signaling pathway has been observed upon CART application (83). (2009) 38:9416. (2012) 44:297301. (1998) 22:114558. It is known that GPCRs participate in almost every process in the regulation of energy homeostasis as well as other physiological processes that are not mentioned in this review. Please Like our Facebook page to support our open-access youth education initiatives! Activation of nuclear factor b by somatostatin type 2 receptor in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells involves G14 and multiple signaling components: a mechanism requiring protein kinase C, calmodulin-dependent kinase II, ERK, and c-Src. (2011) 7:36272. Diabetes. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3290-0, 21. J Pineal Res. The perifornical part of the lateral hypothalamus, which is considered as the feeding center, contains a high density of Y5R that mediates NPY-induced hyperphagia (60). Butler AA, Cone RD. As a result of signal integration from various autocrine/paracrine factors, hormone secretions from endocrine cells are adjusted, and hormonal outputs are released into the circulation (3), which can further influence other organs and tissues to maintain homeostasis. Physiol Rev. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.04.010, 59. Figure 2. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.150, 40. Caicedo A. Paracrine and autocrine interactions in the human islet: more than meets the eye. The protomers within these dimers exhibit different signaling effects that range from facilitation, inhibition, and even modification of the pathways (75). J Physiol. x}Oo0Mc1/x c6IvCFWS)a-h Change), You are commenting using your Facebook account. J Pineal Res. Stimulating -cell replication and improving islet graft function by GPR119 agonists. doi: 10.1039/b823059e, 96. doi: 10.1038/nrn2493, 84. J Biol Chem. (2014) 57:1899910. In classical endocrine systems, hormones are released into the bloodstream and they modify target cells in a distant part of the body; it has become apparent that these processes are regulated by cellular communications encompassing autocrine, paracrine, intracrine, and juxtacrine interactions. Ellacott KLJ, Cone RD. Neuropeptides. The overlapping downstream pathways allow further integration of different messages. 8 0 obj endobj Besides, NPY neurons produce another orexigenic peptide, the agouti-related peptide (AgRP), as an endogenous antagonist to the MC3R and MC4R (80). doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.10.006, 69. The insulin output from -cell (green) is adjusted by an integration of paracrine signals from both - and -cells within the niche. Juxtacrine similarly to paracrine signals also acts on nearby tissues and cells, but the main difference in juxtacrine signalling is that cells releasing juxtacrine signals REQUIRE physical contact with the cell that they are acting upon. There are two main differences between autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine signaling: location and speed. Gao J, Tian L, Weng G, Bhagroo NV, Sorenson RL, O'Brien TD, et al. Glucagon and acetylcholine from -cell (beige), and somatostatin from -cell (blue) are stimulatory and inhibitory signals for hormone secretion, respectively, that can act in both autocrine and paracrine manners via their receptors (GCGR for glucagon; M1R, M3R, and M5R for acetylcholine; SSTR2 and SSTR5 for somatostatin). Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. It should be noted that signal crosstalk and transactivation linkages between GPCR and non-PCR pathways constitute yet another layer of signaling complexity in energy homeostasis (11). stream The expression of type 1 and type 2 melatonin receptors (MT1R and MT2R) in the human islets has been confirmed by molecular and immunocytochemical approaches (32).