Photo credit: Amanda McCreless. (Ed.) [7]:739740 The abdomen of the earwig is flexible and muscular.
var gaJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ?
As with Hemimeridae, they are blind and wingless, with filiform segmented cerci.
and constantly turns and cleans them, preventing fungus diseases.
[20] For protection from predators, the species Doru taeniatum of earwigs can squirt foul-smelling yellow liquid in the form of jets from scent glands on the dorsal side of the third and fourth abdominal segment. They have simple, slender antennae and biting mouth-parts.
), Kuhlmann, Ulrich.
Some examples are the flowers, hops, red raspberries,[58] and corn crops in Germany, and in the south of France, earwigs have been observed feeding on peaches and apricots. "The Relationships of the Tyroglyphoid Mite, Histiostoma Polypori (Oud.)
 [44] Amongst the most frequently suggested order of insects to be the closest relatives of Dermaptera is Notoptera, theorized by Giles in 1963. Click here to see examples of more earwigs! This page was last edited on 18 July 2022, at 04:31. General characteristics:
[44] Amongst the most frequently suggested order of insects to be the closest relatives of Dermaptera is Notoptera, theorized by Giles in 1963. Click here to see examples of more earwigs! This page was last edited on 18 July 2022, at 04:31. General characteristics:
The nymphs feed on food regurgitated by the mother,[22] and on their own molts.
To obtain permission, request it here. if it is hungry enough. These resemble the familiar wing cases of beetles and are also called. incomplete development (egg, nymph, adult)
If the mother dies before the nymphs are ready to leave, the nymphs may eat her. Dermaptera comes from the Greek words derma, which means skin, and ptera, which means wings.
Species have been found to be blind and living in caves, or cavernicolous, reported to be found on the island of Hawaii and in South Africa. and eat a wide variety of plant and animal material.
In species of winged earwigs, the wings will start to develop at this time.
and its Licensors
about 1,800, Classification: Found in caves or near ice or snow at high elevations in mountains of Asia and North America. References Observed prey include largely plant lice, but also large insects such as bluebottle flies and woolly aphids.
One species of tachinid fly, Triarthria setipennis, has been demonstrated to be successful as a biological control of earwigs for almost a century.
[13] Earwigs are characterized by the cerci, or the pair of forceps-like pincers on their abdomen; male earwigs generally have more curved pincers than females. [19], The neuroendocrine system is typical of insects. To obtain permission, request it here. This earwig has has a pair of large claw-like cerci at the end of its abdomen.
[24]
The mother may assist the nymphs in hatching.
Strong neuron connections connect the neurohemal corpora cardiaca to the brain and frontal ganglion, where the closely related median corpus allatum produces juvenile hormone III in close proximity to the neurohemal dorsal arota.
earwigs.
The first epizoic species of earwig was discovered by a London taxidermist on the body of a Malaysian hairless bulldog bat in 1909, then described by Karl Jordan.
Afterward the female will begin to lay 20 to 80 pearly white eggs in two days. However the name most likely comes from the term
[7]:738739, The forewings are short oblong leathery plates used to cover the hindwings like the elytra of a beetle, rather than to fly.
Approximately 4 family and 20 species in North America and 10 family and ~1800 species worldwide. A female will lay hers eggs in a burrow she has excavated or in They feed on a wide variety of plant or animal matter . By the 1950s, the two suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina had been added to Dermaptera.
in length. Oops! Some species can squirt this fluid up to 100 mm (4 inches).
Most earwigs measure between 0.16 to 3.2 inches (4 to 78 millimeters) in length, without the pinchers (PIN-churs), or grasping claws.
Dermaptera is relatively small compared to the other orders of Insecta, with only about 2,000 species, 3 suborders and 15 families, including the extinct suborders Archidermaptera and Eodermaptera with their extinct families Protodiplatyidae, Dermapteridae, Semenoviolidae, and Turanodermatidae.
Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness", "St Helena giant earwig Labidura herculeana", "The evolution of wing folding and flight in the Dermaptera (Insecta)", "Maternal Food Regurgitation to Nymphs in Earwigs (Forficula auricularia)", "Chemical defense of an earwig (Doru taeniatum)", "EENY088/IN245: Ringlegged Earwig, Euborellia annulipes (Lucas) (Insecta: Dermaptera: Carcinophoridae)", "When the Body Hides the Ancestry: Phylogeny of Morphologically Modified Epizoic Earwigs Based on Molecular Evidence", "Evolutionary history of Polyneoptera and its implications for our understanding of early winged insects", "Family-group Names for Earwigs (Dermaptera)", 10.1206/0003-0082(2007)539[1:FNFED]2.0.CO;2, "A phylogeny of earwigs (Insecta: Dermaptera) based on molecular and morphological evidence: reconsidering the classification of Dermaptera", "Vulgar dialect names of earwigs used in Kansai Region, Japan", "Extract - George's Marvellous Medicine by Roald Dahl", The earwigs of California (Order Dermaptera), https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Earwig&oldid=1098925807, Articles containing Old English (ca. I would like to return to the start of this key.
[20], The reproductive system of females consist of paired ovaries, lateral oviducts, spermatheca, and a genital chamber. Some earwigs have defensive glands on the second or third abdominal segment that release a noxious liquid. [27] During the summer they can be found around damp areas such as near sinks and in bathrooms. Reproduction of material from any KnowYourInsects.org webpages without written permission is strictly prohibited.
[11], Most earwigs are flattened (which allows them to fit inside tight crevices, such as under bark) with an elongated body generally .mw-parser-output .frac{white-space:nowrap}.mw-parser-output .frac .num,.mw-parser-output .frac .den{font-size:80%;line-height:0;vertical-align:super}.mw-parser-output .frac .den{vertical-align:sub}.mw-parser-output .sr-only{border:0;clip:rect(0,0,0,0);height:1px;margin:-1px;overflow:hidden;padding:0;position:absolute;width:1px}750 millimetres (142in) long. (1978) Dermaptera Forficulidae European Earwig.
winged (although some are wingless)
are able to store sperm for several months before fertilisation.
Terms of Use, Earwigs: Dermaptera - Behavior And Reproduction, Earwigs: Dermaptera - Physical Characteristics, Behavior And Reproduction, Earwigs And People, European Earwig (forficula Auricularia): Species Accounts - GEOGRAPHIC RANGE, HABITAT, DIET, CONSERVATION STATUS. The phylogeny of the Dermaptera is still debated.
General characteristics:
[14] The theorized stem group of the Dermaptera are the Protelytroptera, which are similar to modern Blattodea (cockroaches) with shell-like forewings and the large, unequal anal fan, are known from the Permian of North America, Europe and Australia. biting mouthparts (chewing mandibles)
are commonly found in dark, sheltered environments and are common 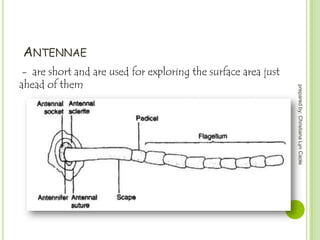 In some species, the forceps have been observed in use for holding prey, and in copulation.
In some species, the forceps have been observed in use for holding prey, and in copulation.
The mother will also faithfully defend the eggs from predators, not leaving them to eat unless the clutch goes bad.
Order Dermaptera This refers to the leathery forewings, which are typical of earwigs.
ra]
[7]:739 After mating, the sperm may remain in the female for months before the eggs are fertilized. During their development, the nymphs' wings grow and the antennae gain extra segments.
The cerci The antennae (an-TEH-nee), or sense organs, are long, thin, and threadlike. Interaction with earwigs at this time results in a defensive free-fall to the ground followed by a scramble to a nearby cleft or crevice.
Life Cycle Most species
[37] The eggs and nymphs are also cannibalized by other earwigs. var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("UA-8758792-1"); [16][29], Earwigs are generally nocturnal, and typically hide in small, dark, and often moist areas in the daytime. of Australia and many species frequent suburban backyards and homes.
Female earwigs usually remain in the nest burrow and care for their eggs and young nymphs.
"); from 5 to 50 millimetres in length. [27], The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting arthropods.
} catch(err) {}. var gaJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ? The large cerci are a characteristic of this order. and may often be attracted to lights at night. [31] Their primary insect predators are parasitic species of Tachinidae, or tachinid flies, whose larvae are endoparasites.
pageTracker._trackPageview(); The wings are not present in all species.
[38] A species of tyroglyphoid mite, Histiostoma polypori (Histiostomatidae, Astigmata), are observed on common earwigs, sometimes in great densities;[39] however, this mite feeds on earwig cadavers and not its live earwig transportation.
[2] Entomologists suggest that the origin of the name is a reference to the appearance of the hindwings, which are unique and distinctive among insects, and resemble a human ear when unfolded. The pinchers of the adult male are larger and thicker than those of the females and young earwigs or larvae (LAR-vee).
[17] The mother has been shown to pick up wax balls by accident, but they would eventually be rejected as they do not have the proper scent. The nymphs mature in late summer. A few species may be predatory.
try { Order Dermaptera: the earwigs
Etymology: var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("UA-8758792-1");
If this doesn't appear to be the order for your insect, go back through the key and look more carefully at your insect while answering the questions again.
[45] A 2018 phylogenetic analysis found that their closest living relatives were angel insects of the order Zoraptera, with very high support.
Gardeners tend not to like them due to their fondness for nibbling at flowers such as Dahlias.
are often used to hold food and carry prey after it has been killed.
Earwigs are described as having front wings called tegmina that are leathery. Most species hardly fly.
If this doesn't appear to be the order for your insect, go back through the key and look more carefully at your insect while answering the questions again.
Your perseverance will reward you!
List of Orders
Photo credit: Amanda McCreless. All of these insects are adapted for a parasitic or semi-parasitic lifestyle: they are secondarily wingless and the cerci are not well-developed into pincers. The male and female will live in a chamber in debris, crevices, or soil 2.5 centimetres (1in) deep. HomeWho We Are
Most earwigs have little or no economic importance.
She prevents fungal damage to the eggs by licking them daily. They can be found in tight crevices in woodland, fields and gardens. Hind wings are large, fan-shaped and pleated. Even though most earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, they are rarely seen in flight.
No fossils from the Triassic during which Dermaptera would have evolved from Protelytroptera have been found.
[3][4] The name is more popularly thought to be related to the old wives' tale that earwigs burrowed into the brains of humans through the ear and laid their eggs there.
They pump blood by elastic connective tissue, rather than muscle.
However, they are omnivorous and eat many pest species.
They must then disperse to new areas or risk being eaten by her. [7]:739740[17] When first laid, the eggs are white or cream-colored and oval-shaped, but right before hatching they become kidney-shaped and brown. under rocks, logs and the bark of trees.
The earwigs attacked mature plants and made cup-shaped bite marks 311mm (18716in) in diameter. [6], Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the Americas and Eurasia.
", Marshall, Judith A. In August 1755 they appeared in vast numbers near Stroud, Gloucestershire, UK, especially in the cracks and crevices of "old wooden buildingsso that they dropped out oftentimes in such multitudes as to literally cover the floor.
Earwigs are sometimes confused
[30], Earwigs are regularly preyed upon by birds, and like many other insect species they are prey for insectivorous mammals, amphibians, lizards, centipedes, assassin bugs, and spiders. with a distinctive tooth near the middle of the inner edge. If the nymphs do not leave the burrow after one or two molts, they are likely to be eaten by their mother. The family includes one very common species, Euborellia annulipes.
[14] The antennae are thread-like with at least 10 segments. brown with straw coloured markings. Class Insecta
Most adult earwigs have four wings. The forceps tend to be more curved in males than in females. hard, elongate body
with the Earwig, Forficula Auricularia Linn. These pincers are used in grooming, defense, courtship, and even to help fold the hind wings. The cerci also gradually assume an adult form. Their liking of moist crevices and rotting vegetation often brings them into contact with humans! And they have membranous hind wings.
Earwig A few species are metallic green. [14], Some evidence of early evolutionary history is the structure of the antennal heart, a separate circulatory organ consisting of two ampullae, or vesicles,[48] that are attached to the frontal cuticle near the bases of the antennae. [7]:740[23].
(26 Aug 2009) "Ocytata pallipes (Falln) (Dipt., Tachinidae), a potential agent for the biological control of the European earwig.
These structures are not used aggressively, but are used to defend territory.
The Dermaptera contains three suborders.
http://genent.cals.ncsu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/id_audio_Dermaptera.mp3. In the Arixeniina, family Arixeniidae, species of the genus Arixenia are normally found deep in the skin folds and gular pouch of Malaysian hairless bulldog bats (Cheiromeles torquatus), apparently feeding on bats' body or glandular secretions.
[17], Female earwig in her nest with newly hatched young, The eggs hatch in about seven days. Wan X, Kim MI, Kim MJ, Kim I (2012) Complete mitochondrial genome of the free-living earwig, "Phylum Arthropoda von Siebold, 1848 In: Zhang, Z.-Q.
Legs are thin and adapted for running.
} catch(err) {}, Kingdom Animalia Contact Us The scientific name for the order, "Dermaptera", is Greek in origin, stemming from the words derma, meaning skin, and pteron (plural ptera), wing.
[54] Earwigs have been rarely known to crawl into the ears of humans,[55] but they do not lay eggs inside the human body or human brain as is often claimed. Earwigs
document.write(unescape("%3Cscript src='" + gaJsHost + "google-analytics.com/ga.js' type='text/javascript'%3E%3C/script%3E")); If this doesn't appear to be the order for your insect, go back through the key and look more carefully at your insect while answering the questions again.
dark-colored
Like most other epizoic species, there is no fossil record, but they are probably no older than late Tertiary.
Species within Forficulina are free-living, have functional wings and are not parasites. [18], Earwigs are among the few non-social insect species that show maternal care.
Unless noted otherwise, photographs on this website are the property of the photographers and may not be reused without written permission from the photographers. Earwigs are nocturnal [7]:740 Another distinct maternal care unique to earwigs is that the mother continuously cleans the eggs to protect them from fungi.
Your perseverance will reward you! [59], Dimick, R.E. [41], The fossil record of the Dermaptera starts in the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic period about 208million years ago in England and Australia, and comprises about 70 specimens in the extinct suborder Archidermaptera. For a list of all of the orders in this key, click here: List of Orders. "https://ssl." var pageTracker = _gat._getTracker("UA-8758792-1"); Unless noted otherwise, photographs on this website are the property of the photographers and may not be reused without written permission from the photographers.
They have been known to cause economic losses in fruit and vegetable crops. One of the distinctive features that you can see on the illustration associated with this insect order is the presence of forceps at the end of the abdomen. Members of this family are found all over Australia. Labidura riparia is the only member of this family found in the United States.