The most common are the alpha ()-helix and beta ()-pleated sheet structures. If the protein is subject to changes in temperature, pH, or exposure to chemicals, the protein structure may change, losing its shape in what is known as denaturation as discussed earlier. e State one function of each molecule. Examples of biological macromolecules include carbohydrates and proteins both of which are essential for life to survive. Although cholesterol is often spoken of in negative terms, it is necessary for the proper functioning of the body. The large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromolecules. The albumin protein in the liquid egg white is denatured when placed in a hot pan, changing from a clear substance to an opaque white substance. Organogenesis and Vertebrate Formation, Chapter 2: Introduction to the Chemistry of Life. For example, insulin is a protein hormone that maintains blood glucose levels. Which disgram best represents the arrangement of water molecules around sodium (Na+) and Chlorine (Cl-) ions, Science Fusion Ohio Student Edition Worktext Grade 8. Red blood cells (RBCs) in this sense are exceptional. Some fatty acids have common names that specify their origin. In addition, registered dietitians must complete a supervised internship program and pass a national exam. #related-posts { var relatedpoststitle="Related Posts"; The unique sequence for every protein is ultimately determined by the gene that encodes the protein. For an additional perspective on lipids, explore Biomolecules: The Lipids through this interactive animation. The polysaccharides or complex carbohydrates represent the form that sugar takes when it is stored. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. The resulting bond is the peptide bond. For example, palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid, is derived from the palm tree. For example hemoglobin is a globular protein but collagen found in our skin is a fibrous protein. Carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants. Ribosomes are structures found in the cytoplasm of cells that build proteins. Hormones are chemical signaling molecules, usually proteins or steroids, secreted by an endocrine gland or group of endocrine cells that act to control or regulate specific physiological processes, including growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. Animal Nutrition and the Digestive System, Chapter 22. Lipids are hydrophobic (water-fearing), or insoluble in water, because they are nonpolar molecules. The unique sequence and number of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. What are the parts of a hemoglobin molecule?
The former types of interactions are also known as hydrophobic interactions. What is most remarkable to consider is that a hemoglobin molecule is made up of two alpha chains and two beta chains that each consist of about 150 amino acids. Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions, 24.3. Fats and oils are usually made up of fatty acids and glycerol. Plants are able to synthesize glucose, and the excess glucose is stored as starch in different plant parts, including roots and seeds. The flowers look different, but the bulbs look very similar. Folding patterns resulting from interactions between the non-R group portions of amino acids give rise to the secondary structure of the protein. Cells store energy for long-term use in the form of lipids called fats. Any of the hydrogen atoms can be replaced with another carbon atom covalently bonded to the first carbon atom.
Hemoglobin | Human anatomy and physiology | Health & Medicine | Khan Academy, Matter Changes State Because Of Pressure Temperature And What, In What Organelles Do Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Take Place. adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []; margin-top: 0em; The three fatty acids in the fat may be similar or dissimilar. text-transform: none; Is hemoglobin a fibrous or globular protein? To isolate the fat, the fish is boiled and the floating fat skimmed off. The heat acts like our pancreatic amylase enzyme and breaks down the long chains of inulin into digestible mono and di-saccharides. The most common disaccharide is sucrose, or table sugar, which is composed of the monomers glucose and fructose. Instead of three fatty acids attached, however, there are two fatty acids and the third carbon of the glycerol backbone is bound to a phosphate group. }, no: 7 in mcqs the answer cannot be C. as ice is actually less dense than water (liquid state) that is why ice floats on waterthnxx. Protein shape is critical to its function and this shape is maintained by many different types of chemical bonds. Animal fats with stearic acid and palmitic acid contained in meat, and the fat with butyric acid contained in butter, are examples of saturated fats. Like fats, they are composed of fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol or similar backbone. Name the subatomic particle that participates in chemical bond formation. Fats. In plants, fat or oil is stored in seeds and is used as a source of energy during embryonic development. Cellulose is made up of glucose monomers that are linked by bonds between particular carbon atoms in the glucose molecule. Osmotic Regulation and Excretion, Chapter 24. For example, hemoglobin is a combination of four polypeptide subunits. Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides. letter-spacing: 2px; In monosaccharides, the number of carbon atoms usually ranges from three to six. A fat molecule, such as a triglyceride, consists of two main componentsglycerol and fatty acids. For example, scientists have determined that human cytochrome c contains 104 amino acids. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (CH4), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom. a major constituent of the membranes of cells; composed of two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to the glycerol backbone, a long chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, a long chain of monosaccharides; may be branched or unbranched, a biological macromolecule composed of one or more chains of amino acids, a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides that is involved in protein synthesis, a long-chain hydrocarbon with single covalent bonds in the carbon chain; the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton is maximized, a type of lipid composed of four fused hydrocarbon rings, a form of unsaturated fat with the hydrogen atoms neighboring the double bond across from each other rather than on the same side of the double bond, a fat molecule; consists of three fatty acids linked to a glycerol molecule, Chapter 3: Introduction to Cell Structure and Function, Chapter 4: Introduction to How Cells Obtain Energy, Chapter 5: Introduction to Photosynthesis, Chapter 6: Introduction to Reproduction at the Cellular Level, Chapter 7: Introduction to the Cellular Basis of Inheritance, Chapter 8: Introduction to Patterns of Inheritance, UNIT 3: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY, Chapter 9: Introduction to Molecular Biology, Chapter 10: Introduction to Biotechnology, Chapter 11: Introduction to the Bodys Systems, Chapter 12: Introduction to the Immune System and Disease, Chapter 13: Introduction to Animal Reproduction and Development, Chapter 14. The cell walls of plants are mostly made of cellulose, which provides structural support to the cell. In fact. Because of this change of one amino acid in the chain, the normally biconcave, or disc-shaped, red blood cells assume a crescent or sickle shape, which clogs arteries. Fats and oils are a stored form of energy and can include triglycerides.
A hemoglobin molecule is made up of four polypeptide chains two alpha chains of 141 amino acid residues each and two beta chains of 146 amino acid residues each. } What is TRUE about haemoglobin ? font-size: 18px; In these animals, certain species of bacteria reside in the rumen (part of the digestive system of herbivores) and secrete the enzyme cellulase. Preface to the original textbook, by OpenStax College, 3.2 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, 4.3 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation, 4.5 Connections to Other Metabolic Pathways, 5.2: The Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis, 8.3 Extensions of the Laws of Inheritance, 10.2 Biotechnology in Medicine and Agriculture, 20.2 Gas Exchange across Respiratory Surfaces, 20.4 Transport of Gases in Human Bodily Fluids, 21.4. They often work with patients in health-care facilities, designing nutrition plans to prevent and treat diseases. The polysaccharides or complex carbohydrates represent the form that sugar takes when it is stored. Protein sequencing has shown that there is a considerable amount of sequence similarity among cytochrome c molecules of different species; evolutionary relationships can be assessed by measuring the similarities or differences among various species protein sequences. The nature of its fat also made it an important trade good. Under which circumstances is it more useful to use the MO model? padding-left:5px; Each enzyme is specific for the substrate (a reactant that binds to an enzyme) upon which it acts. The Evolutionary Significance of Cytochrome cCytochrome c is an important component of the molecular machinery that harvests energy from glucose. float:center; Registered dietitians help plan food and nutrition programs for individuals in various settings.
Globin a complex macromolecule is a protein that helps to keep the hemoglobin liquefied. Disaccharides (di- = two) form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction (a reaction in which the removal of a water molecule occurs). Animal Reproduction and Development, Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition, Next: Chapter 3: Introduction to Cell Structure and Function, Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Describe the ways in which carbon is critical to life, Explain the impact of slight changes in amino acids on organisms, Describe the four major types of biological molecules, Understand the functions of the four major types of molecules, Figure 2.16 by Ken Bosma is licensed under a, Figure 2.22 by OpenStax is licensed under a. Carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, depending on the number of monomers in the molecule. Consequently, they must be supplemented through the diet. The fatty acid chains are hydrophobic and exclude themselves from water, whereas the phosphate is hydrophilic and interacts with water. Enzymes, which are produced by living cells, are catalysts in biochemical reactions (like digestion) and are usually proteins. Every other glucose monomer in cellulose is flipped over and packed tightly as extended long chains. This helps in my revision a lot <3. Glycerol is an organic compound with three carbon atoms, five hydrogen atoms, and three hydroxyl (OH) groups. Each hemoglobin molecule is made up of four heme groups surrounding a globin group forming a tetrahedral structure. The R groups are attached to the carbons, and extend above and below the folds of the pleat. Fertilization and Early Embryonic Development, 24.7. Ooligan fat composition is 30% saturated fat (like butter) and 55% monounsaturated fat (like plant oils). Galactose (part of lactose, or milk sugar) and fructose (found in fruit) are other common monosaccharides. An example of an enzyme is salivary amylase, which breaks down amylose, a component of starch. During this covalent bond formation, three water molecules are released. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. It is composed of two strands, or polymers, of nucleotides. > It also is rich in three fat soluble vitamins A, E and K. Unlike the phospholipids and fats discussed earlier, steroids have a ring structure. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which an acidic carboxyl group is attached, hence the name fatty acid. The number of carbons in the fatty acid may range from 4 to 36; most common are those containing 1218 carbons. Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation, 22.2. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds. font-weight: bold; Cellulases can break down cellulose into glucose monomers that can be used as an energy source by the animal. Which do you expect will be paramagnetic due to the presence of unpaired electrons? Inulin is used as dietary fibre however, it is not readily digested by humans. They also provide insulation for the body. In addition, they may contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and additional minor elements. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cells mass. The heme contains iron and transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues as well as takes carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. Hemoglobin is an oxygen transport protein found in vertebrates. Each cell in a living system may contain thousands of different proteins, each with a unique function. Hint: Hemoglobin is abbreviated as Hb where it is consists of two parts named heme and globulin and found in the red blood cells and it is useful to carry the oxygen from the lungs to the body parts and helps for aerobic respiration.
Normally an individual has four genes that code for the alpha protein or alpha chain. They are a type of polyunsaturated fat and are called omega-3 fatty acids because the third carbon from the end of the fatty acid participates in a double bond.
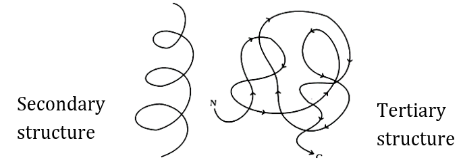
Lipids perform many different functions in a cell. Simply speaking, hydrogen gas is bubbled through oils to solidify them. Waxes are made up of a hydrocarbon chain with an alcohol (OH) group and a fatty acid. It is a globular protein with a quaternary structure (has four subunits): 2 alpha. The DNA molecules never leave the nucleus, but instead use an RNA intermediary to communicate with the rest of the cell. Fats serve as long-term energy storage. font-family: Arial Narrow; The molecule, therefore, has about 600 amino acids. Carbohydrates serve other functions in different animals. Each protein has its own unique sequence and shape held together by chemical interactions. } Protein shape is critical to its function. I work at Camosun College located in beautiful Victoria, British Columbia with campuses on the Traditional Territories of the Lekwungen and WSNE peoples. height:100%; margin-bottom: 0.75em; Foundations of Physical Science (Florida Edition). [2], galactose correctly drawn; [2], Carbon atoms need not be numbered. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. Registered Dietitian: Obesity is a worldwide health concern, and many diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease, are becoming more prevalent because of obesity. The -helix and -pleated sheet structures are found in many globular and fibrous proteins. The information needed to build hemoglobin is stored in the form of a gene (DNA). It is also the precursor of vitamins E and K. Cholesterol is the precursor of bile salts, which help in the breakdown of fats and their subsequent absorption by cells. Its composition is said to make it as healthy as olive oil, or better as it has omega 3 fatty acids that reduce risk for diabetes and stroke. A long chain of monosaccharides linked by covalent bonds is known as a polysaccharide (poly- = many). DNA is the genetic material found in all living organisms, ranging from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals.
Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet; grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources of carbohydrates. Lipids include a diverse group of compounds that are united by a common feature. Plants synthesize glucose using carbon dioxide and water by the process of photosynthesis, and the glucose, in turn, is used for the energy requirements of the plant.
Proteins may be structural, regulatory, contractile, or protective; they may serve in transport, storage, or membranes; or they may be toxins or enzymes. } Saturated fats tend to get packed tightly and are solid at room temperature. Examples of antigens include microorganisms (bacteria fungi parasites and viruses) and chemicals. The sequence and number of amino acids ultimately determine a proteins shape, size, and function. (A) It is a dipeptide and present in red blood corpuscles in blood worm. A nucleic acid is a long molecule made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides. When the hydrocarbon chain contains a double bond, the fatty acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. Lipids. Importantly it is a solid grease at room temperature. Proteins are organized at four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. This exoskeleton is made of the biological macromolecule chitin, which is a nitrogenous carbohydrate. Although glucose, galactose, and fructose all have the same chemical formula (C6H12O6), they differ structurally and chemically (and are known as isomers) because of differing arrangements of atoms in the carbon chain. Polysaccharides are. Not all proteins are denatured at high temperatures; for instance, bacteria that survive in hot springs have proteins that are adapted to function at those temperatures. Starch is the stored form of sugars in plants and is made up of amylose and amylopectin (both polymers of glucose). Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Cholesterol is mainly synthesized in the liver and is the precursor of many steroid hormones, such as testosterone and estradiol. A hemoglobin molecule is made up of, 2 Haemoglobin. Omega-3 fatty acids fall into this category and are one of only two known essential fatty acids for humans (the other being omega-6 fatty acids). Examples of hydrophilic globular protein macromolecules include hemoglobin in the blood and enzymes. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the molecular orbital model and the crystal field model. The R group is the only difference in structure between the 20 amino acids; otherwise, the amino acids are identical. While the terms polypeptide and protein are sometimes used interchangeably, a polypeptide is technically a polymer of amino acids, whereas the term protein is used for a polypeptide or polypeptides that have combined together, have a distinct shape, and have a unique function.
Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. Polysaccharides may be very large molecules. Human Reproductive Anatomy and Gametogenesis, 24.4. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Watch a video about proteins and protein enzymes. Write ground-state electron configurations for the ions Be+, C-, Ne2+, Mg+, P2+, CI-, As+, and I- . Isovaleric acid beta-hydroxybutyric acid glutaric acid and asparagine have shown positive effects and the butyrate is unusually potent for hemoglobin production (Table 2). var defaultnoimage="http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-PpjfsStySz0/UF91FE7rxfI/AAAAAAAACl8/092MmUHSFQ0/s1600/no_image.jpg"; Mammals store fats in specialized cells called adipocytes, where globules of fat occupy most of the cell. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of the plasma membrane. Proteins are one of four classes of biochemical compounds which are compounds in living things. Weak interactions between the subunits help to stabilize the overall structure. In the food industry, oils are artificially hydrogenated to make them semi-solid, leading to less spoilage and increased shelf life. The chemical nature of the R group determines the chemical nature of the amino acid within its protein (that is, whether it is acidic, basic, polar, or nonpolar).